The Essential Guide to Grain Drying: Maximizing Your Harvest's Potential

In the world of agriculture, grain drying is a pivotal procedure that can significantly impact the quality and profitability of a farmer's harvest. Adequate drying not only preserves the integrity of the grain but also enhances its marketability. This article delves into the importance, methods, benefits, and considerations of grain drying, enabling farmers to make informed decisions that align with their operational goals.
1. Understanding Grain Drying
Grain drying refers to the process of reducing the moisture content of harvested grains to a suitable level. High moisture content can lead to a myriad of issues, including:
- Storage Mold: Excess moisture creates a hospitable environment for mold, leading to spoilage.
- Insect Infestation: Damp grains attract pests, which can cause significant losses.
- Quality Degradation: Wet grains often suffer from deterioration, affecting taste and nutritional value.
The goal of grain drying is to bring moisture levels down to a safe range, typically between 12% and 14%, depending on the type of grain.
2. The Importance of Grain Drying in Agriculture
The impact of effective grain drying on farming cannot be overstated. Here are several critical reasons why it deserves attention:
- Preservation of Grain Quality: Properly dried grains maintain their nutritional value, flavor, and texture.
- Maximized Storage Life: Reduced moisture minimizes spoilage and extends the storability of the grain.
- Increased Market Value: High-quality, well-preserved grains fetch better prices in the market, directly impacting profitability.
- Compliance with Standards: Many markets have strict moisture content standards; adhering to these ensures market access.
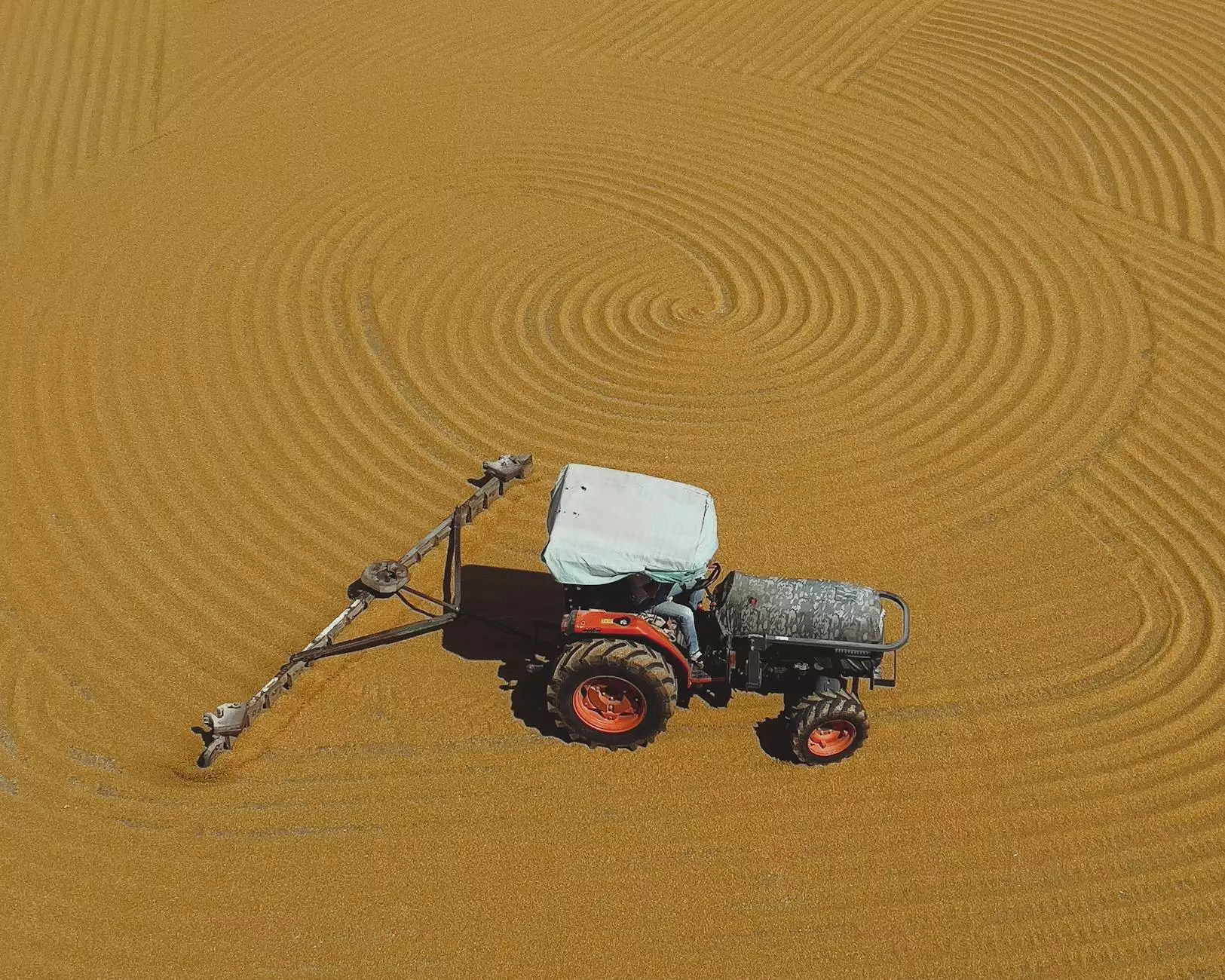
3. Methods of Grain Drying
Farmers can choose from a variety of grain drying methods depending on their resources, grain type, and scale of operation:
3.1 Natural Drying
This traditional method relies on the sun and wind to reduce moisture content. Grains can be spread out in thin layers on clean, dry surfaces or stored in well-ventilated areas. Some advantages include:
- Low cost and minimal investment.
- Environmentally friendly with no energy costs.
However, weather variability can lead to inconsistent drying results, making this less reliable in certain climates.
3.2 Mechanical Drying
In contrast, mechanical drying employs various equipment, such as grain dryers, to control the drying process. Here’s a closer look:
- Batch Dryers: Ideal for small-scale operations, these allow for manual control of grain moisture levels.
- Continuous Flow Dryers: Efficient for larger operations, these systems continuously move grain through a drying chamber.
- Heat and Airflow Control: Advanced systems offer precise control over temperature and airflow, ensuring even drying.
The initial costs may be higher for mechanical drying; however, the efficiency and improved grain quality often justify the investment.
3.3 Infrared and Microwave Drying
These methods utilize electromagnetic waves to quickly remove moisture from grains. They are characterized by:
- Rapid drying times.
- Minimal energy consumption.
- Preservation of grain nutrients due to lower temperature exposure.
However, these methods may not be widely adopted yet due to costs and equipment availability.
4. Factors Influencing Grain Drying
Several factors influence the effectiveness and efficiency of the grain drying process:
4.1 Grain Type
Different grains have varying moisture absorption and drying characteristics. Common grains and their optimal moisture content include:
- Wheat: 12-14%
- Corn: 15-20%, ideally 15%
- Rice: 12-14%
4.2 Ambient Conditions
Humidity, temperature, and airflow conditions significantly affect drying. Warmer, less humid conditions enhance drying efficiency. Monitoring local weather patterns can improve decision-making regarding when to dry grains.
4.3 Equipment Efficiency
The efficiency of drying equipment can play a vital role in the successful removal of moisture. Regular maintenance and upgrading old machines can increase drying speeds and reduce energy usage.
5. Best Practices for Effective Grain Drying
To maximize the benefits of grain drying, farmers should adopt the following best practices:
- Regular Monitoring: Track the moisture content frequently to determine the exact drying needs.
- Appropriate Harvest Timing: Harvest grains when they are at optimal moisture levels to minimize drying time.
- Utilizing Quality Equipment: Investing in reliable and efficient grain dryers can save time and resources.
- Storing Dried Grain Correctly: Ensure grains are stored in dry, cool, and well-ventilated locations to maintain quality.
6. The Economic Impact of Grain Drying
Understanding the economic role of grain drying can help farmers appreciate its value beyond mere preservation of harvest quality:
6.1 Cost Savings
Effective grain drying can lead to significant cost savings by reducing losses associated with spoilage and pest infestations. Additionally, better quality grains demand higher prices in the market.
6.2 Increased Yield Returns
Enhancing grain quality through proper drying can increase market access. High-quality products open doors to premium markets, further boosting potential sales revenues.
7. Conclusion: Embracing the Future of Grain Drying
As agriculture continually evolves, grain drying remains a cornerstone of successful farming. With advancements in technology and a deeper understanding of drying techniques, farmers can better preserve their harvest and optimize their profits. By prioritizing effective grain drying methods, farmers not only protect their current assets but also pave the way for future sustainability in agricultural practices.
For farmers looking for high-end equipment support, the grain drying services offered by TSGC Inc. can provide the necessary resources and expert guidance to ensure efficient and effective grain drying processes. By investing in knowledge and superior equipment, you are setting the foundation for a profitable and sustainable agricultural future.